Ovulation tests are a valuable tool for women trying to conceive, offering insights into the fertile window by detecting the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that precedes ovulation. However, understanding their accuracy and how they work is essential for maximizing their effectiveness.
Ovulation tests function by identifying the level of LH in the urine. LH is a hormone that plays a key role in the reproductive system, and its concentration spikes just before ovulation. When an ovulation test detects this spike, it indicates that ovulation is likely to occur within the next 24 to 36 hours. Some tests may also measure estrogen levels, adding another layer of accuracy to the prediction. These tests typically involve dipping a test strip into a urine sample and waiting for the results to appear as lines or symbols, similar to a pregnancy test.
Measuring Accuracy of Ovulation Tests
Accuracy in the context of ovulation tests is generally defined in terms of sensitivity and specificity.
Sensitivity: The ability of the test to correctly identify the presence of an LH surge.
Specificity: The test’s ability to correctly rule out the absence of an LH surge.
Common sensitivity for over-the-counter ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) is 20-40 mIU/mL of LH. These levels strike a balance between detecting the LH surge with a reasonable degree of accuracy while minimizing false positives. Kits with 20 mIU/mL sensitivity are more sensitive and can detect lower LH levels, beneficial for individuals with smaller LH surges, while those with 30-40 mIU/mL are suitable for those with more pronounced LH surges.
Most commercially available ovulation tests boast an accuracy rate of about 99% in detecting the LH surge when used correctly. This high accuracy rate indicates their effectiveness in predicting ovulation. However, it is vital to understand what this statistic implies: a 99% accuracy rate means that in 99 out of 100 cases, the test will correctly indicate an LH surge when it occurs.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
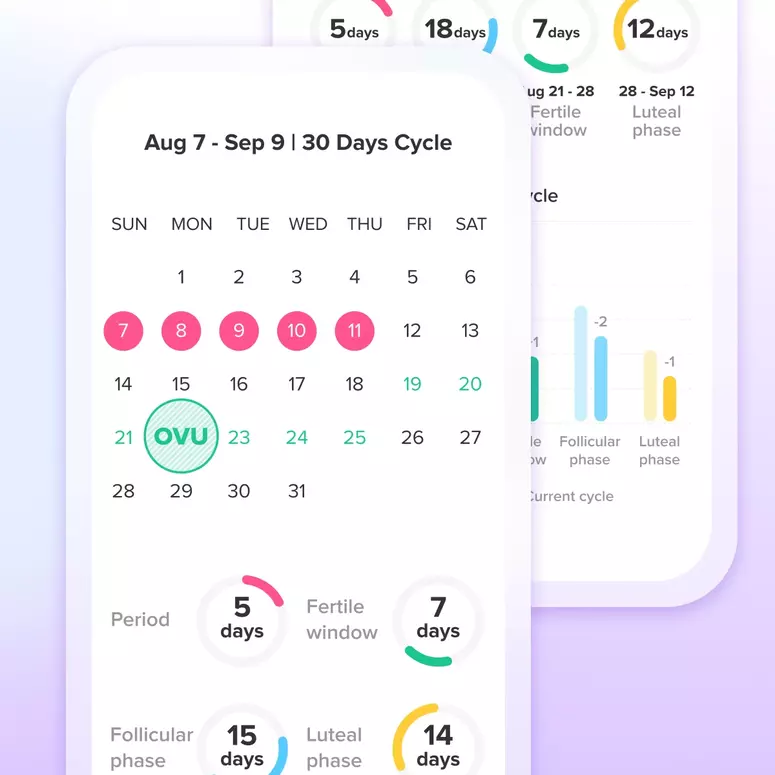
Timing of the Test Within the Menstrual Cycle: The timing of the test plays a crucial role in its accuracy. LH surges typically occur around the middle of the menstrual cycle, about 24 to 36 hours before ovulation. Testing too early or too late in the cycle can lead to missed surges or false negatives.
Variations in Individual LH Levels: Individual differences in LH levels can affect test results. Some individuals may have naturally lower or higher LH surges, making it challenging for the test to detect. Those with conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) might have consistently elevated LH levels, leading to false positives.
Correct Usage of the Test: Proper usage according to the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial for obtaining accurate results. Reading the test results too early or too late can lead to misinterpretation. Additionally, ensuring that the test is not exposed to moisture, contaminants, or improper storage conditions is essential for maintaining its accuracy.
Can Ovulation Tests be Wrong?
Ovulation tests can produce false positives or false negatives due to various factors:
False positives can occur due to cross-reactivity with similar hormones like FSH, TSH, LH, and hCG, luteinized unruptured follicle (LUF) syndrome, PCOS, pregnancy, and certain medications.
False negatives can result from low LH levels that don’t meet the test’s threshold or incorrect testing times.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Accuracy
Here are some practical tips to help ensure you get the most reliable ovulation test results:
Read the Instructions Carefully: Each ovulation test brand may have slightly different instructions. Ensure you read and follow the specific guidelines included with your test.
Test at the Same Time Each Day: Consistency is key. It’s generally recommended to test around the same time each day to get the most consistent results.
Limit Fluid Intake Before Testing: Avoid excessive drinking for about two hours before taking an ovulation test, as this can dilute your urine and make the LH surge harder to detect.
Combine with Other Methods: Women with irregular cycles may find ovulation tests less reliable, as predicting the fertile window becomes more challenging. In such cases, combining ovulation tests with other methods, like basal body temperature tracking, can improve accuracy.
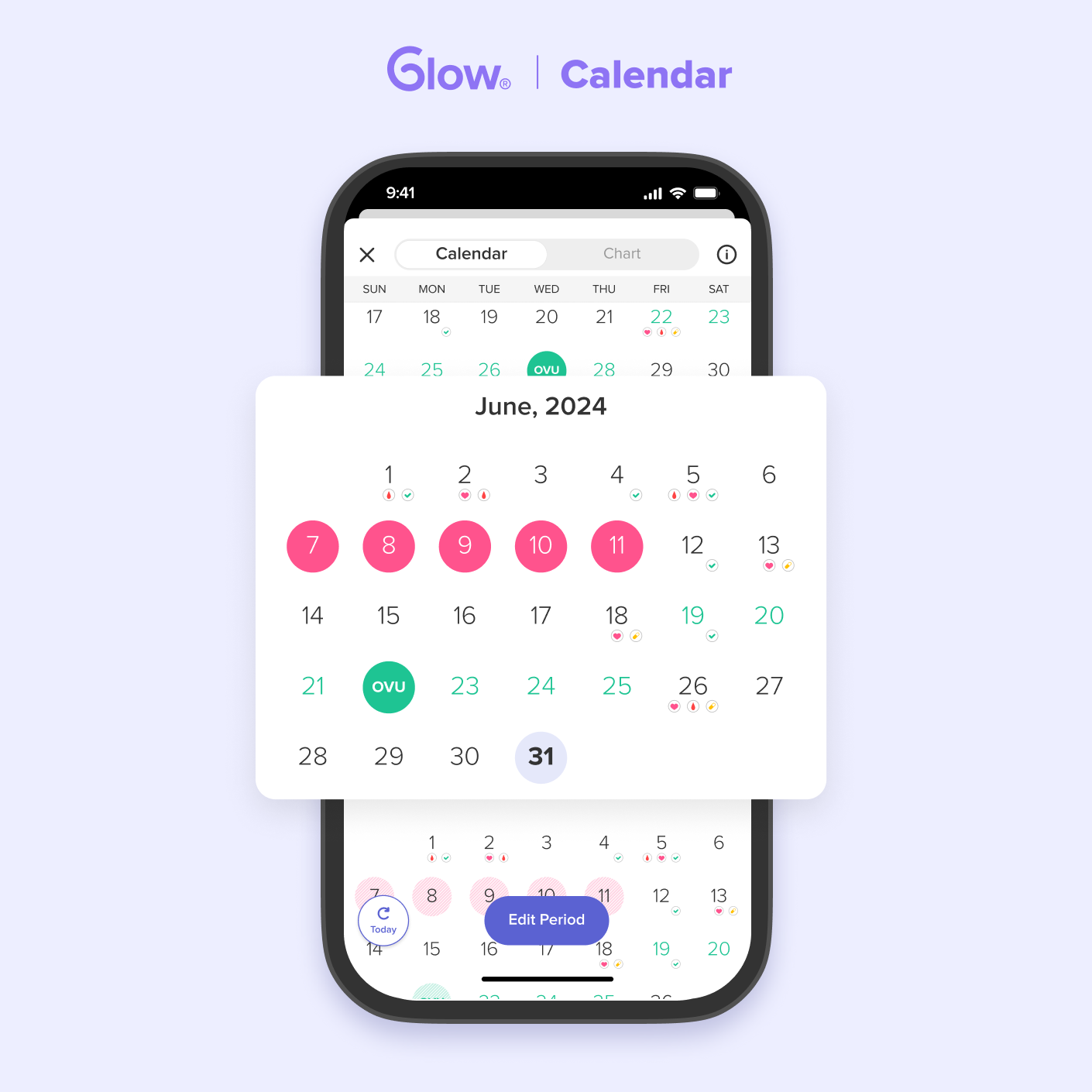
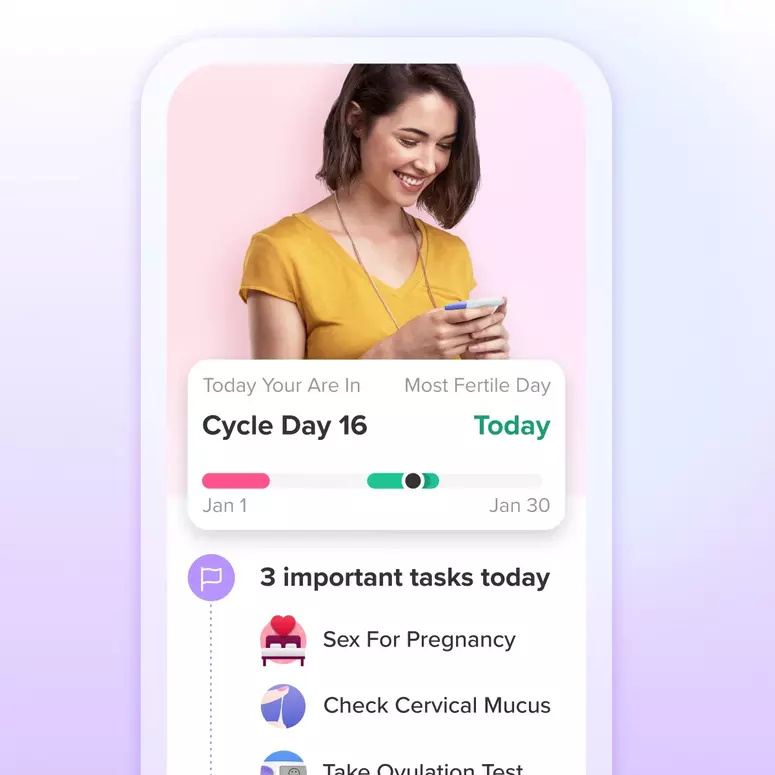
Using the Glow App: Glow helps you understand your cycle pattern and predict your fertile window, making it easier to plan your ovulation tests. The app also sends you reminders when it’s time to test.